Joint replacement surgery is a medical procedure designed to relieve pain and improve function in a joint that has been damaged by conditions such as arthritis, injuries, or degenerative diseases. While the decision to undergo joint replacement surgery can be daunting, it is often a life-changing solution for individuals who experience chronic pain and reduced mobility. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what joint replacement surgery entails, the types of joint replacement procedures, what to expect before, during, and after surgery, as well as the recovery process.
What Is Joint Replacement Surgery?
Joint replacement surgery involves removing a damaged or worn-out joint and replacing it with a prosthetic or artificial joint made of metal, plastic, or ceramic components. The goal of the procedure is to alleviate pain, restore function, and improve the quality of life for the patient.
The most common joints that are replaced include:
Hip replacement
Knee replacement
Shoulder replacement
Ankle replacement
Elbow replacement
The decision to opt for joint replacement surgery is typically made after conservative treatments, such as medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes, have failed to provide relief.
Types of Joint Replacement Surgery
1. Hip Replacement (Hip Arthroplasty)
This procedure involves replacing the damaged hip joint with a prosthetic. Hip replacement surgery is commonly recommended for patients suffering from osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or hip fractures that result in chronic pain and immobility. There are two types of hip replacement surgeries:
Total Hip Replacement (THR): The entire hip joint is replaced, including the femoral head (the ball) and the acetabulum (the socket).
Hip Resurfacing: A less invasive alternative where the damaged parts of the femoral head are shaved and capped with metal components.
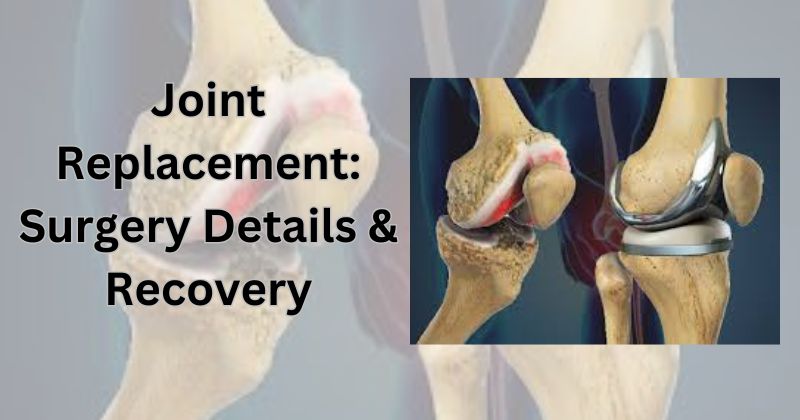
2. Knee Replacement (Knee Arthroplasty)
Knee replacement surgery is performed when the knee joint becomes severely damaged by arthritis or injury. The surgery may involve replacing the entire knee joint or just part of it:
Total Knee Replacement (TKR): The entire knee joint is replaced with a prosthetic, including the femur, tibia, and patella.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR): Only the damaged portion of the knee is replaced, leaving the healthier parts of the knee intact.
3. Shoulder Replacement (Shoulder Arthroplasty)
Shoulder replacement surgery is performed to relieve pain and restore function in patients with rotator cuff tears, arthritis, or fractures. The procedure can involve replacing the ball (humeral head) and/or the socket (glenoid) of the shoulder joint.
Total Shoulder Replacement: Both the ball and socket are replaced with artificial components.
Reverse Shoulder Replacement: This is an option for patients with severe rotator cuff damage, where the positions of the ball and socket are reversed.
4. Ankle Replacement (Ankle Arthroplasty)
Ankle replacement surgery is typically recommended for patients with severe arthritis or injury in the ankle joint. The surgery involves replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one to reduce pain and improve mobility.
5. Elbow Replacement (Elbow Arthroplasty)
Elbow replacement is typically performed for patients with joint damage due to arthritis, fractures, or other conditions. This procedure involves replacing the damaged parts of the elbow with an artificial prosthetic joint.
What to Expect Before Joint Replacement Surgery
Consultation and Pre-Surgical Assessment
Before undergoing joint replacement surgery, your doctor will assess your overall health and determine if you’re a suitable candidate for the procedure. This typically involves:
Physical examination: To assess joint function and mobility.
Medical history review: To understand any pre-existing conditions that may affect the surgery or recovery.
Imaging tests: X-rays or MRI scans to evaluate the extent of joint damage.
Blood tests: To check for any underlying health issues that may complicate the surgery.
Your doctor will also discuss the type of joint replacement surgery that is most appropriate for your condition.
Preparing for Surgery
Once you’re cleared for surgery, there are a few steps you’ll need to follow:
Medications: You may be advised to stop taking certain medications before the surgery, including blood thinners or anti-inflammatory drugs.
Diet: You may be required to fast for 12 hours before the surgery.
Arrangements: Make sure you have someone to assist you during your recovery, as you may not be able to move around independently for the first few days.
The Joint Replacement Surgery Procedure
The procedure for joint replacement surgery typically follows these steps:
Anesthesia: General or regional anesthesia is administered to ensure you’re comfortable and pain-free during the procedure.
Incision: A small incision is made near the damaged joint to access the area.
Joint Removal: The damaged parts of the joint are carefully removed. For hip or knee replacements, this typically involves removing the femoral head or the damaged part of the knee joint.
Implantation: The prosthetic joint, which is custom-fit for the patient, is inserted. It is typically made from a combination of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials designed to mimic the natural movement of the joint.
Closing the Incision: Once the new joint is in place, the incision is closed with stitches or staples, and a sterile bandage is applied.
Recovery: After the surgery, the patient is monitored as they wake from anesthesia. Physical therapy often begins the same day or the day after surgery to help with movement and prevent complications like blood clots.
Recovery After Joint Replacement Surgery
After joint replacement surgery recovery, the process is crucial to ensure proper healing and regain mobility. The timeline and specific steps will vary based on the type of joint replaced, but the general recovery process includes:
1. Hospital Stay
Most patients stay in the hospital for about 1 to 4 days after surgery, depending on the type of surgery and any complications. During this time, you will begin physical therapy to regain joint movement and strength.
2. Pain Management
Pain management is a priority during recovery. You will be given pain medications to keep you comfortable, but it’s essential to follow your doctor’s guidelines on dosages to avoid complications.
3. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is a critical part of the recovery process. It helps improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the new joint. Rehabilitation begins early, often within the first 24-48 hours after surgery, and can last for several weeks to months. Therapy will gradually become more intense as your body heals.
4. Resuming Daily Activities
Most patients can return to daily activities like walking, driving, and light exercise within 3-6 weeks after surgery. However, high-impact activities like running or heavy lifting may be restricted for several months.
5. Long-Term Recovery
Full recovery can take anywhere from 6 months to a year, depending on the type of surgery and the patient’s age and health. Regular follow-up appointments with your surgeon will be necessary to ensure the joint is functioning properly and there are no complications.
Risks and Complications of Joint Replacement Surgery
While joint replacement surgery has a high success rate, it is not without risks. Potential complications include:
Infection: At the surgical site or deep within the joint.
Blood clots: Especially in the legs (deep vein thrombosis).
Implant failure: In rare cases, the prosthetic joint may loosen, wear out, or break over time.
Nerve or blood vessel injury: During the procedure.
Dislocation or joint stiffness: Particularly in hip and shoulder replacements.
It’s essential to discuss the risks and potential complications with your surgeon to make an informed decision.
Conclusion
Joint replacement surgery is a highly effective procedure for relieving pain and restoring mobility in patients suffering from joint diseases or injuries. By understanding the surgery details, the recovery process, and the potential risks, you can make an informed decision about whether joint replacement is the right solution for you.
If you or a loved one is considering joint replacement surgery, consult with an orthopedic surgeon to discuss your options, and start your journey towards a pain-free, more active life. With proper care, rehabilitation, and lifestyle adjustments, you can enjoy a successful recovery and a return to normal activities.